Researchers in Japan have identified the first spontaneous mutant coral symbiont alga to not maintain a symbiotic relationship with its host.
They have devised a system in which the simple addition or depletion of a nutrient can experimentally switch the symbiosis on and off. The mutant symbiont alga enables development of a genetic transformation system, which will be a powerful tool for studying coral-algal endosymbiosis.
Coral reefs are a major reservoir of biodiversity in the sea. The ecosystem relies on a stable symbiotic relationship between the host cnidarian animals, including corals and sea anemones, and the symbiont dinoflagellate. Ongoing environmental changes due to global warming can collapse the symbiosis: a phenomenon known as ‘coral bleaching.’ In addition, mechanisms for maintaining stable symbiosis are poorly understood, partly due to a lack of research tools.

Figure 1. Coral symbiont alga Symbiodinium and the model cnidarian Exaiptasia pallida. Symbiotic (left) and
non-symbiotic state (right) of the ‘curly’ sea anemone E. pallida.
Credit(著作権): (Shinichiro Maruyama)
‘First we established an efficient method for culturing dinoflagellate cells in our lab,’ said Shinichiro Maruyama, an assistant professor at Tohoku University. ‘Then we cultured the cells in the presence of various drugs and screened for spontaneous drug-resistant mutants to isolate clones useful for symbiosis experiments.’
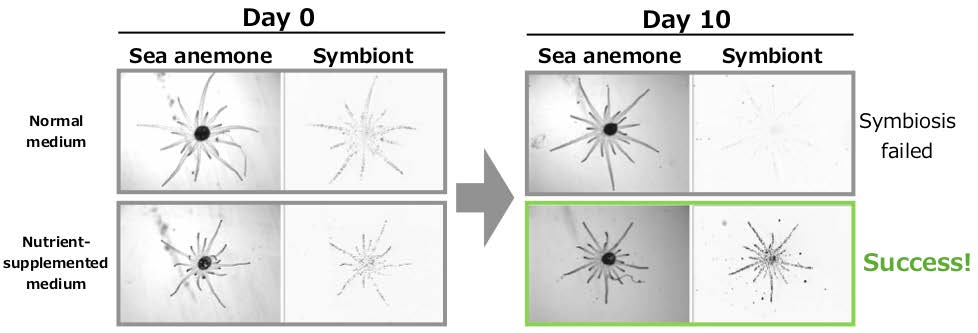
Figure 2. Symbiosis experiments using a mutant algal strain isolated in this study. The addition of a nutrient can lead to symbiosis (modified from Ishii et al.)
Publication Details:
Title: Isolation of uracil auxotroph mutants of coral symbiont alga for symbiosis studies
Authors: Yuu Ishii, Shinichiro Maruyama, Konomi Fujimura-Kamada, Natsumaro Kutsuna, Shunichi Takahashi, Masakado Kawata, Jun Minagawa
Journal: Scientific Reports
Title: Isolation of uracil auxotroph mutants of coral symbiont alga for symbiosis studies
Authors: Yuu Ishii, Shinichiro Maruyama, Konomi Fujimura-Kamada, Natsumaro Kutsuna, Shunichi Takahashi, Masakado Kawata, Jun Minagawa
Journal: Scientific Reports
Embargo date: Feb 19th, 10:00 UK time
Press release in Japanese:
共生できないサンゴ共生藻突然変異株の単離に成功 〜共生のスイッチを操作してオン・オフできる基盤技術を開発〜
共生できないサンゴ共生藻突然変異株の単離に成功 〜共生のスイッチを操作してオン・オフできる基盤技術を開発〜
Contact:
Shinichiro Maruyama
Department of Environmental Life Sciences
Graduate School of Life Sciences
Tohoku University
Email: maruyama@tohoku.ac.jp
Website: https://www.lifesci.tohoku.ac.jp/en/research/teacher/detail.html?id=33636
Shinichiro Maruyama
Department of Environmental Life Sciences
Graduate School of Life Sciences
Tohoku University
Email: maruyama@tohoku.ac.jp
Website: https://www.lifesci.tohoku.ac.jp/en/research/teacher/detail.html?id=33636

