Although water is essential for plant growth, excessive amounts can waterlog and kill a plant. In South and Southeast Asia, where periodic flooding occurs during the rainy season, the water depth can reach several meters for many months.
Rice varieties known as “deepwater rice” have developed a unique strategy to ensure their own survival. Deepwater rice grows normally in shallow water but in heavy floods increases its height in keeping with rising water levels, to enable the plants to ride out lengthy floods. (Figure 1).
A research team comprising Takeshi Kuroha at Tohoku University, Motoyuki Ashikari at Nagoya University, Susan R. McCouch at Cornell University and colleagues in Japan and the U.S.A., have discovered a gene in rice that is critical to its survival in flood conditions. They have also shed light on its molecular function and evolutionary history.
The research group identified the SD1 (SEMIDWARF1), as a key gene responsible for the deepwater rice’s response. The SD1 encodes a biosynthesis enzyme of gibberellin - a plant hormone. The gene orchestrates the deepwater rice response via a unique gain-of-function allele (Figure 2). When submerged, rice accumulate ethylene, a gaseous plant hormone. Deepwater rice amplify a signaling relay in which the SD1 gene is transcriptionally activated by an ethylene-responsive transcription factor, OsEIL1a.
The resulting SD1 protein directs increased synthesis of gibberellins, largely one of gibberellin species, GA4, which promote vertical growth in the plant. Further analysis revealed that this conditionally functional variation evolved first in a wild ancestor and was then a target of selection during the domestication of cultivated rice adapted to deepwater environments in Bangladesh.
The SD1 gene is well-known as the Green Revolution gene in rice, where a loss-of-function allele of SD1 confers short plant height, providing lodging resistance and increases the harvest index, generating greater grain yields under high input agricultural systems (Figure 3- left).
A transcriptional gain-of-function allele of the same gene enables deepwater rice to adapt to flooding via the opposite phenotypic response – an increase in plant height (Figure 3- right). The ability of SD1 to function in such diverse roles in cultivated rice highlights the inherent plasticity of plant response to its environment.
“Extreme weather events caused by climate change could affect food production worldwide,” said Kuroha. “Farmers will need to diversify their methods and the cryptic genetic variation found in wild rice genes may offer adaptive solutions for growing resilient crops.”
Publication Details:
Title: An Ethylene-Gibberellin Signaling Underlies Adaptation of Rice to Periodic Flooding
Authors: Takeshi Kuroha, Keisuke Nagai, Rico Gamuyao, Diane R. Wang, Tomoyuki Furuta, Masanari Nakamori, Takuya Kitaoka, Keita Adachi, Anzu Minami, Yoshinao Mori, Kiyoshi Mashiguchi, Yoshiya Seto, Shinjiro Yamaguchi, Mikiko Kojima, Hitoshi Sakakibara, Jianzhong Wu, Kaworu Ebana, Nobutaka Mitsuda, Masaru Ohme-Takagi, Shuichi Yanagisawa, Masanori Yamasaki, Ryusuke Yokoyama, Kazuhiko Nishitani, Toshihiro Mochizuki, Gen Tamiya, Susan R. McCouch, and Motoyuki Ashikari
Journal: Science
Release date: July 10, 11am
DOI: 10.1126/science.aat1577
Embargo date: 2:00 pm U.S. Eastern Time Thursday, 12 July 2018.
DOI: 10.1126/science.aat1577
Embargo date: 2:00 pm U.S. Eastern Time Thursday, 12 July 2018.
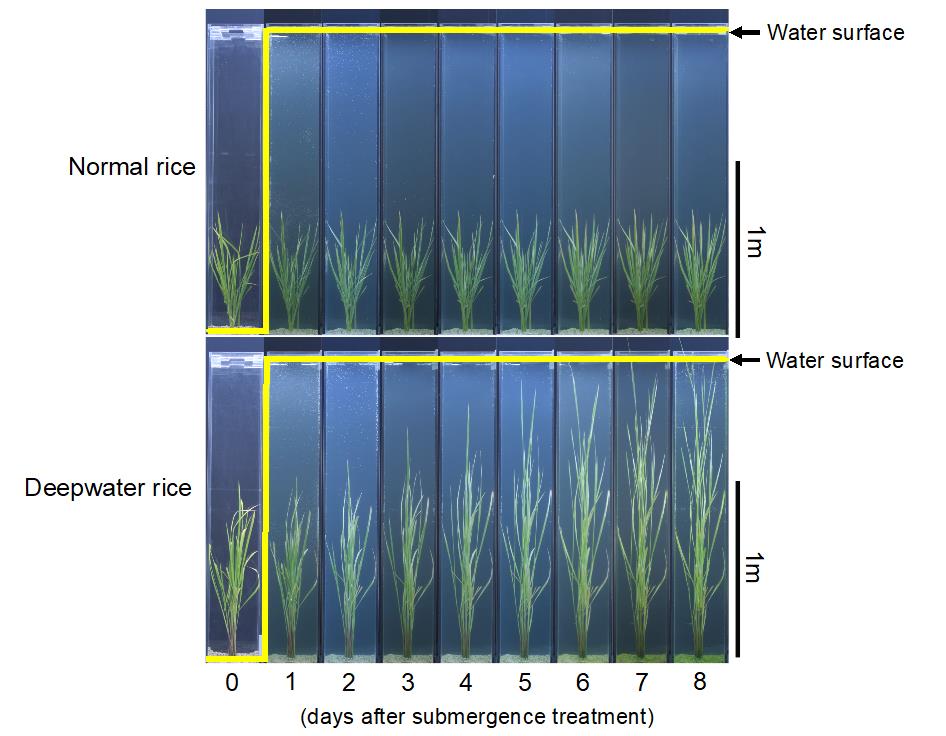
Figure 1
Image title: Temporal morphological changes of rice in deepwater conditions.
Caption:Copyright: Takeshi Kuroha, Keisuke Nagai, and Motoyuki Ashikari
Image title: Temporal morphological changes of rice in deepwater conditions.
Caption:Copyright: Takeshi Kuroha, Keisuke Nagai, and Motoyuki Ashikari
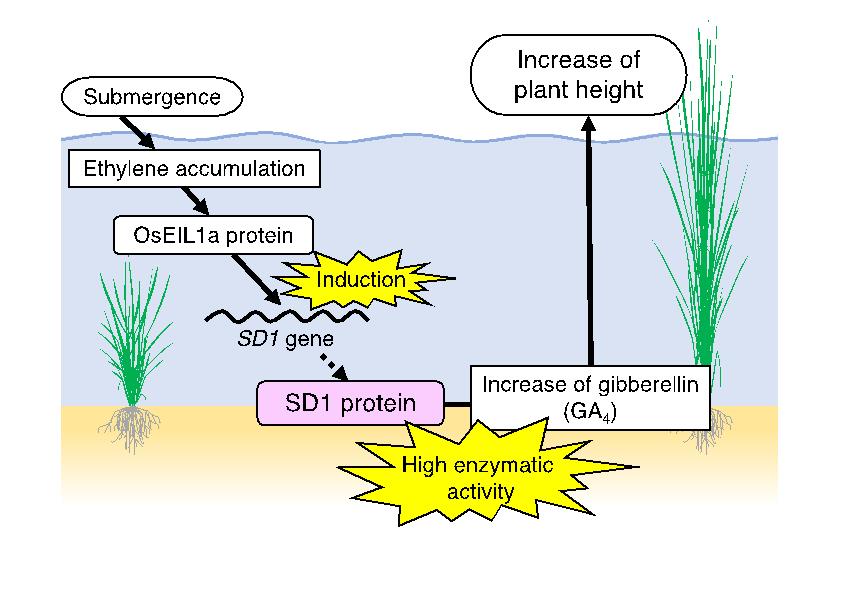
Figure 2
Image title: Molecular mechanism in deepwater rice.
Caption:Copyright: Takeshi Kuroha, Keisuke Nagai, and Motoyuki Ashikari
Image title: Molecular mechanism in deepwater rice.
Caption:Copyright: Takeshi Kuroha, Keisuke Nagai, and Motoyuki Ashikari
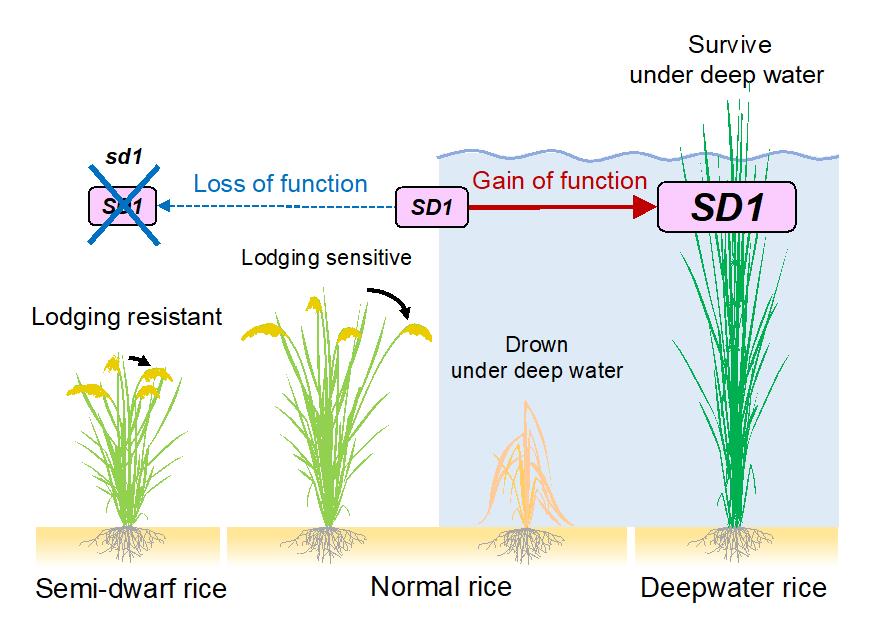
Figure 3
Image title: The SD1 gene enables the plant to adapt to different environments.
Caption: Copyright: Takeshi Kuroha, Keisuke Nagai, and Motoyuki Ashikari
Image title: The SD1 gene enables the plant to adapt to different environments.
Caption: Copyright: Takeshi Kuroha, Keisuke Nagai, and Motoyuki Ashikari
Link:
Contact:
Takeshi Kuroha
Graduate School of Life Sciences
Tohoku University
Email: tkuroha(at)m.tohoku.ac.jp
Graduate School of Life Sciences
Tohoku University
Email: tkuroha(at)m.tohoku.ac.jp

